
Hygroscopic Vs Hydroscopic Moisture Absorption Clearified!
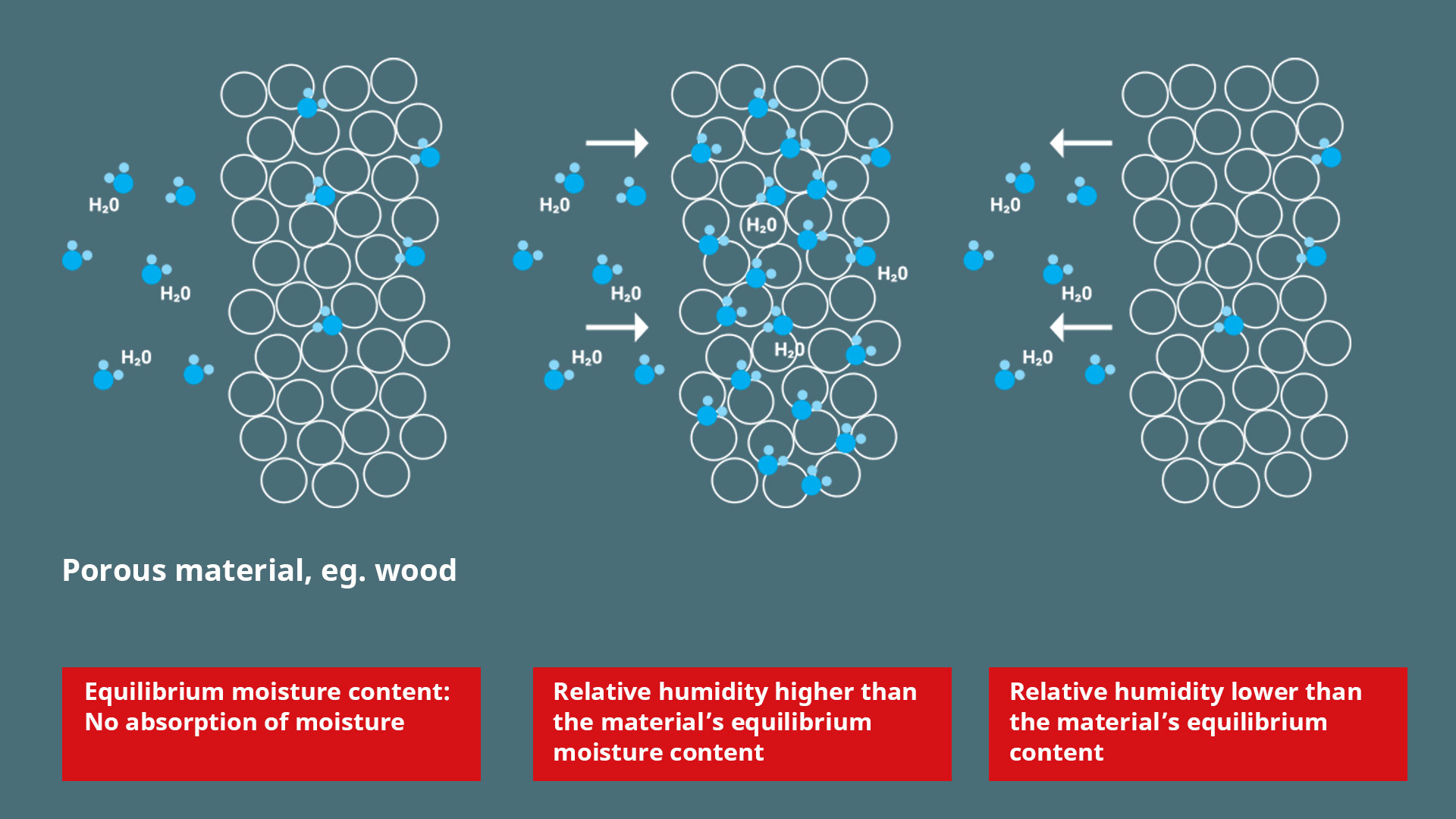
Hygroscopicity, Hygroscopic Constant. Hygroscopicity is the property of small‐particle systems to take up moisture from the atmosphere (Gregorich et al., 2001) through strong sorption forces on the particle surfaces and through capillary condensation due to the lowering of the watervapor pressure above concave capillary menisci.
PPT Chapter 10 Liquids and Solids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5888387
April 17, 2023 by Ozil Hygroscopic vs Hydroscopic: What's the Difference? When it comes to materials science and engineering, the terms "hygroscopic" and "hydroscopic" are often used interchangeably. However, there is a subtle difference between them that can impact the performance and effectiveness of a material in various applications.

A Simple Way of Hygroscopic Testing for Humidity Science
The main difference between hydroscopic and hygroscopic materials is their capacity to absorb moisture. Hydroscopic materials can absorb water from the atmosphere in any physical form, while hygroscopic materials can only absorb moisture in its gaseous form. Understanding the Importance of Hygroscopic and Hydroscopic Materials

PPT Biology Biochemistry Unit Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life PowerPoint Presentation ID5256630
Hygroscopic vs. Hydroscopic You might encounter the word "hydroscopic" used in place of "hygroscopic," however, while hydro- is a prefix meaning water, the word "hydroscopic" is a misspelling and is incorrect. A hydroscope is an instrument used to take deep-sea measurements.
Water Free FullText Water, Soil, and Plants Interactions in a Threatened Environment
1 Hygroscopicity is measure of how much the molecule likes to bond molecules of water, by hydrating/covering charged part of the molecule with molecule/s of water, which relates to it having some polar or charged functional groups, like hydroxyl group for phenols.

PPT Sugar Technology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3709298
Hydroscopic materials are those that have the ability to absorb water. Unlike hygroscopic materials, which absorb moisture from the air, hydroscopic materials absorb water directly. Examples of hydroscopic materials include cotton, wood, and some types of plastics. The ability to absorb water can have both positive and negative effects on these.
Avoid unwanted dessication of products and raw materials
What's the Difference Between Hygroscopic and Hydrophobic Materials? This article was authored by: Jenny Seim Technical Writer Simply stated, hygroscopic materials absorb moisture, whereas hydrophobic materials do not absorb moisture from the environment.

What is Adsorbed water and Hygroscopic water in soil? YouTube
By Abhishek The terms hygroscopic and hydroscopic may sound similar but their meanings completely differ from one another. Hygroscopic substance refers to the substance that can take and hold moisture from the surroundings. Hydroscope is an instrument used to see objects deep underwater.
Differentiate between Hygroscopic water and capillary water.
Resins moved from storage to the molding machine often must be dried because of these properties. They must be processed quickly after drying. Nylon 6 is one of the more hygroscopic resins and is.
Hygroscopic curves, corresponding optical images, and Raman spectra at... Download Scientific
Hygroscopic − R efers to the ability of a material to absorb humidity from the air. A hygroscopic substance will actively attract and absorb water, without bonding. (A hygroscope is an instrument that indicates changes in humidity.)
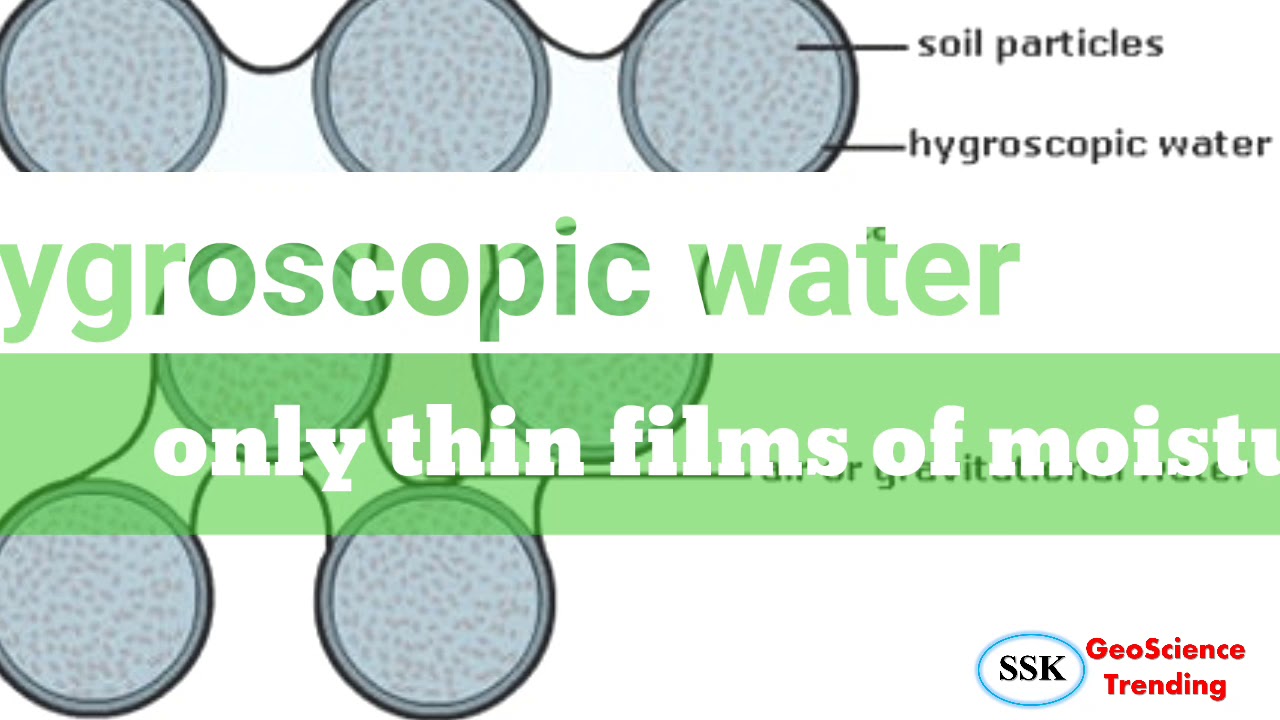
Hygroscopic water YouTube
Hygroscopic vs. Non-Hygroscopic Resins What does hygroscopic mean, and how does it affect resin moisture retention and drying? Hygroscopic Resins (i.e., Nylon, ABS, Acrylic, Polyurethane, Polycarbonate, PET, PBT,) Have a strong affinity to attract moisture Will absorb moisture onto their molecular structure if exposed to ambient air
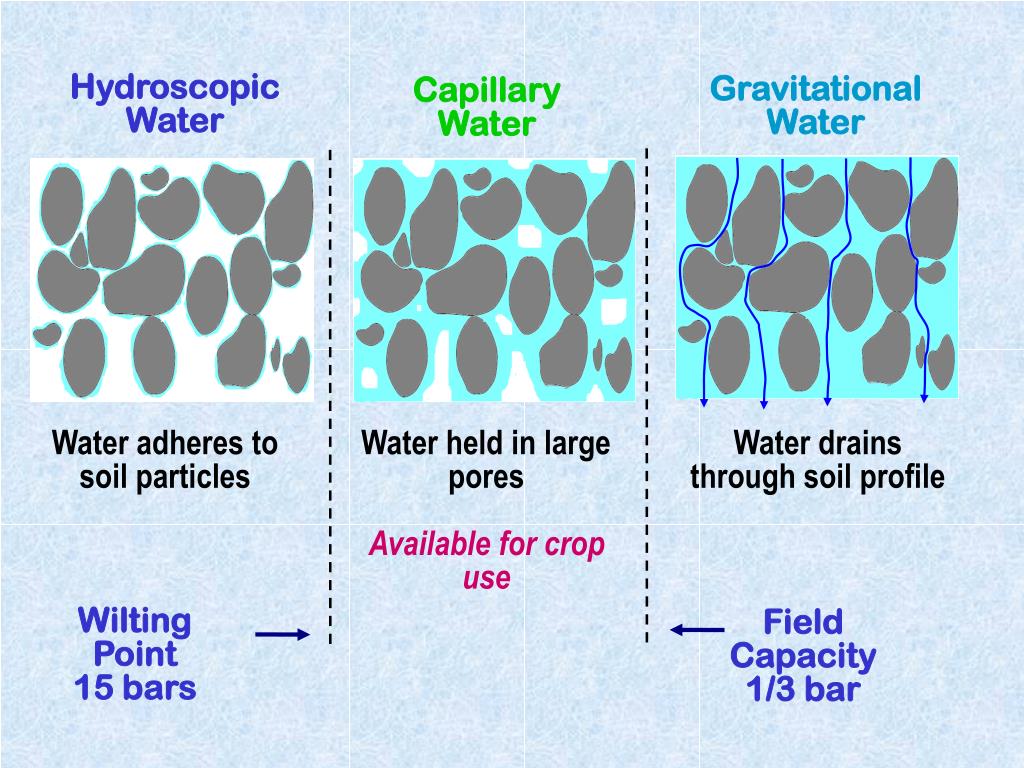
PPT Soil Water PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6408324
Hygroscopic means capable of attracting and holding water from environment, either through absorption or adsorption. Typically, this process occurs near ambient or room temperature. Hygroscopy is the ability to attract and hold water.

Hygroscopic Vs Hydroscopic Moisture Absorption Clearified!
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature.

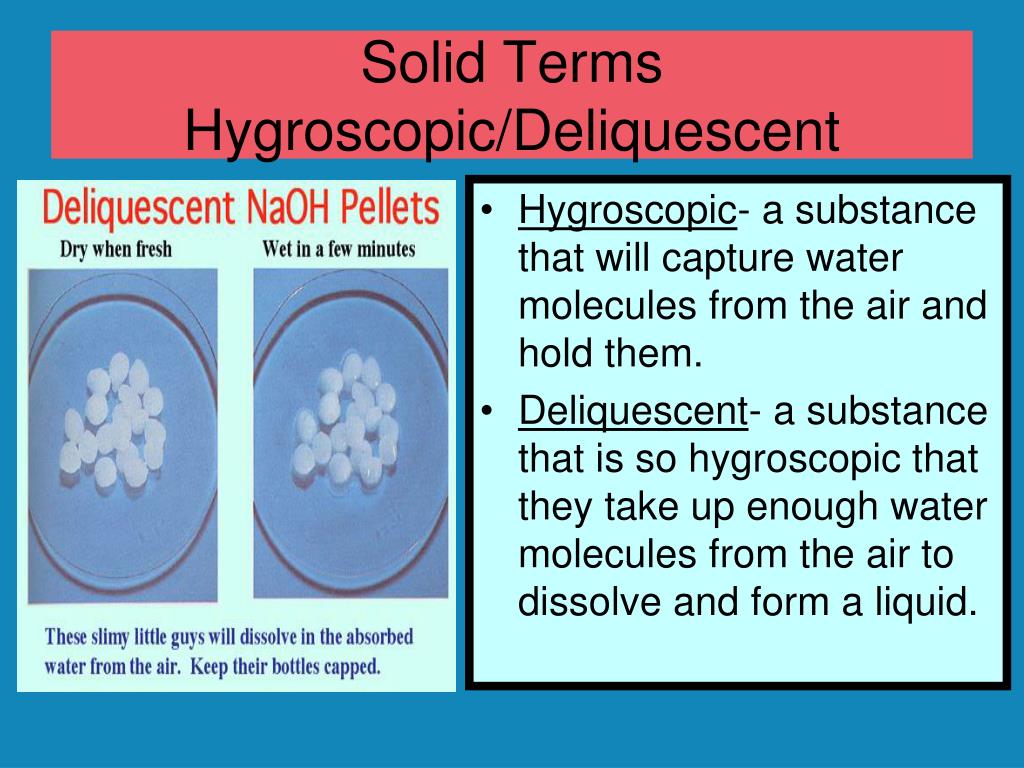
HYGROSCOPICITY HYGROSCOPIC MATERIALS & CLASSIFICATION DETECTION & TESTING DELIQUESCENT
"Hygroscopic" and "Hydroscopic" are two terms that can easily be confused due to their phonetic similarities. However, only "Hygroscopic" is the scientifically accepted term, denoting a substance's ability to attract and hold water molecules from the surrounding environment. This property is vital in many industrial and scientific applications.

Difference Between Deliquescent Efflorescent and Hygroscopic
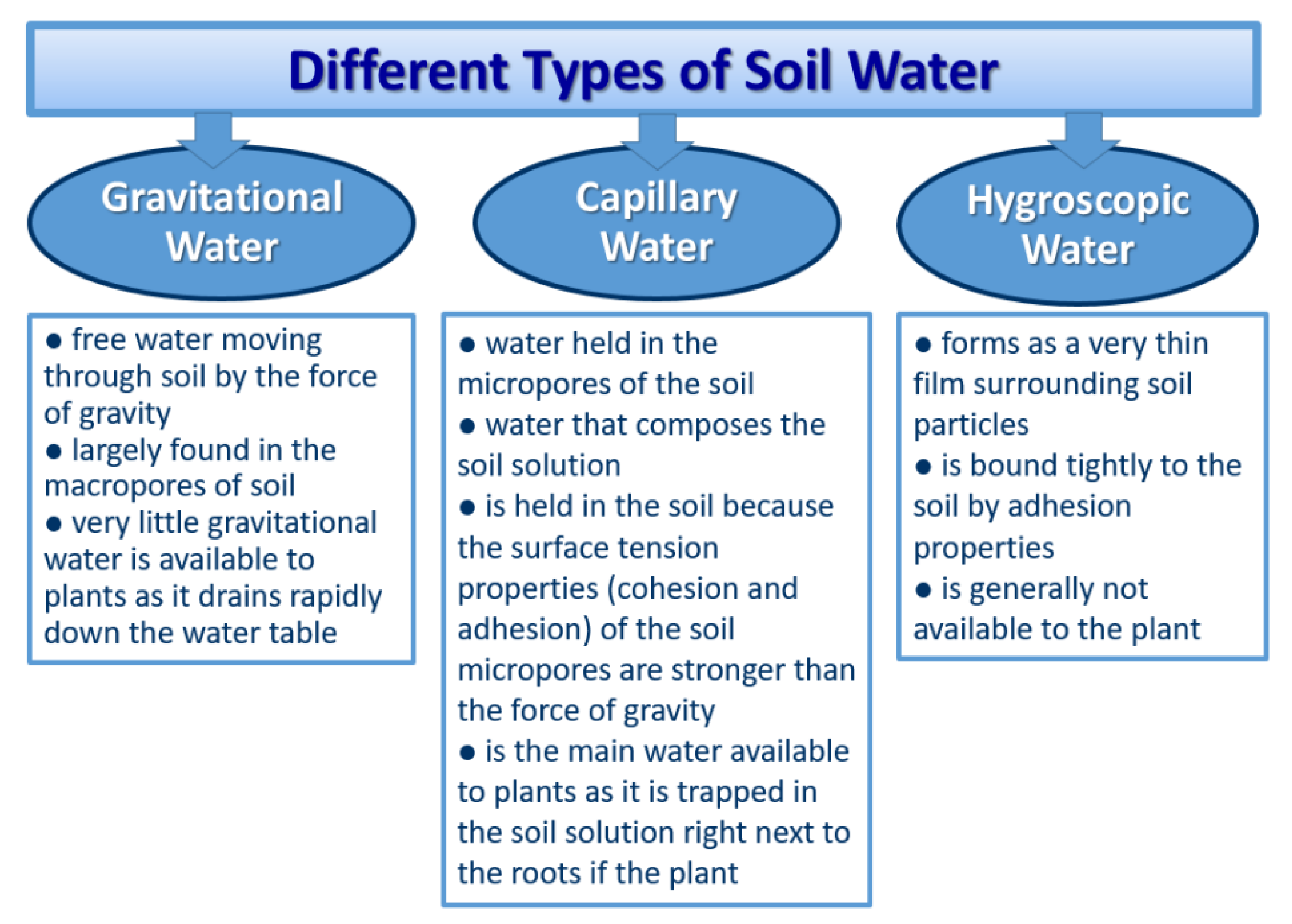
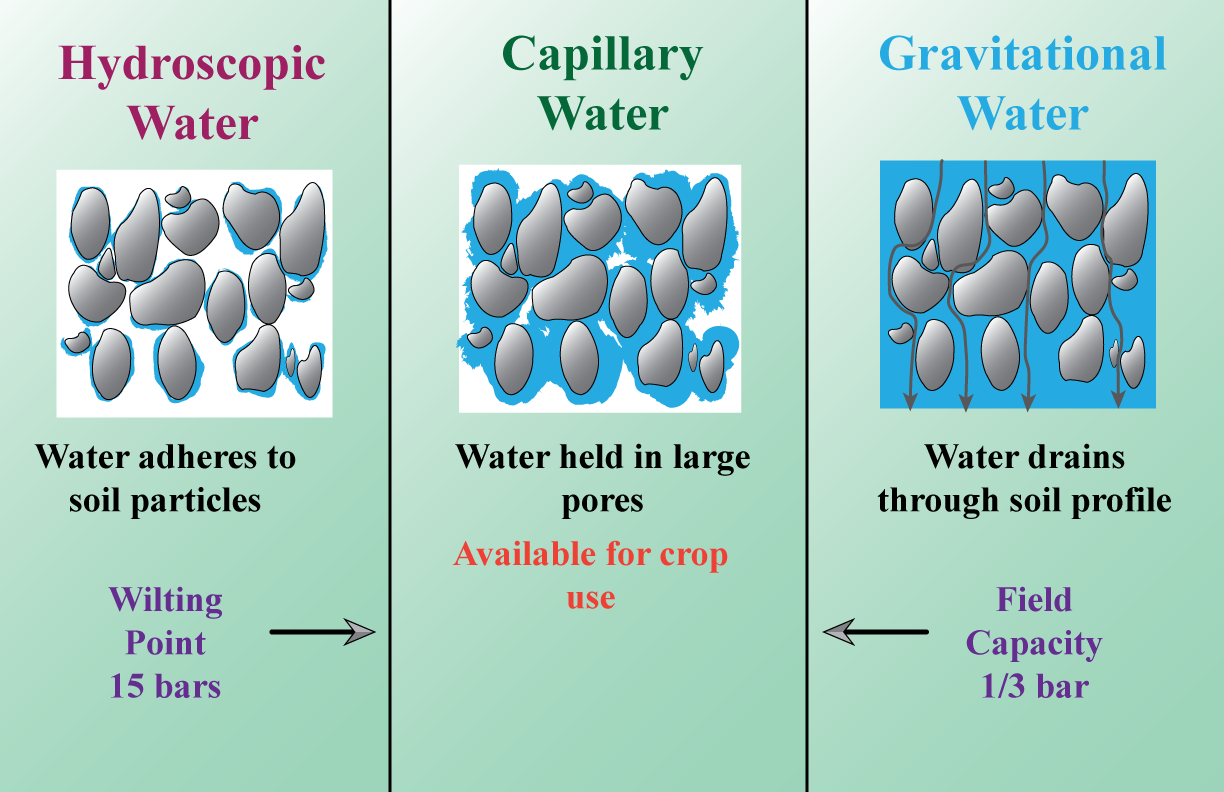
The Hygroscopic Coefficient is the condition when the last micro pore is drained of water and only films of water exist surrounding the soil particles. Soil dried at 105°C to a constant weight is considered oven dry. The oven dry weight of soil is used as the reference weight to quantify the amount of water in mineral soils for all moisture.
Schematic illustration of the hygroscopic mechanism of CSNT particles... Download Scientific
Hygroscopic materials are substances that can absorb water from their surrounding environment. This water could be in the form of humidity or liquid. These materials have a great affinity for water and can even pull water vapor out of the air.